Citrus allergy is a common immune system disorder caused by the body’s increased sensitivity to oranges, tangerines, lemons, pomelos, and other citrus fruits. If the pathology is not detected in time, it can significantly reduce the quality of life and, in some cases, even lead to death. Let’s examine why citrus allergy occurs, and how to diagnose and treat it.
Earlier we wrote about – What a Tick Bite Looks Like and When Symptoms Appear.
Causes of Citrus Allergy in Children and Adults
Allergy to tangerines, limes, oranges, and other citrus fruits is common among people of all ages. It occurs much more frequently than allergic reactions to eggs, fish, and other foods.
The reason for the body’s heightened sensitivity to citrus fruits is the presence of several allergic components in high concentrations. These include amines, salicylates, and benzoates.
Once these allergens enter the bloodstream, the body produces histamine intensively, leading to the rapid development of a food allergic reaction.
Citrus allergy is most often observed in childhood. The causes for its development in this category of patients are:
- Incomplete immune system formation: In the first years of life, children’s immunity continues to develop, making them more prone to allergic reactions than adults.
- Genetic predisposition: If one of the parents is allergic to oranges, grapefruits, or other citrus fruits, the likelihood increases that the child will also suffer from it.
- Negative environmental impact: In regions with high radiation levels, polluted air, and water, the risk of developing allergic reactions increases.
- Early introduction to the diet: Due to the high concentration of allergenic substances, doctors recommend introducing citrus fruits to children after they turn one year old, or sometimes even later. This is because the body of a young child may not be ready to encounter the allergens found in these fruits.
Citrus allergy in many children gradually disappears as they grow older. However, there are cases where it bothers a person in adulthood. The reasons for this may include:
- Weak immune system: Due to this, the body’s defenses cannot work correctly and react violently to allergens entering the bloodstream from citrus fruits.
- Gastrointestinal diseases: In some people, citrus allergy can result from chronic gastritis, irritable bowel syndrome, and other inflammatory processes in the digestive system. In this case, against the background of the inflammation of the disease, symptoms characteristic of allergic reactions appear.
- Long-term use of medications containing citrus components: If you consume oranges, lemons, or other fruits simultaneously with such medications, it can provoke the development of hypersensitivity reactions.
- Genetic predisposition: In adulthood, as in childhood, individual intolerance to oranges and lemons is often determined by heredity. The risk of developing an allergy is higher in people whose parents or grandparents have increased sensitivity to these products.
Sometimes an allergic reaction to citrus in children and adults develops due to the overconsumption of tangerines, oranges, and other fruits. The body receives a large number of allergens it cannot “process,” leading to a malfunction. Excessive histamine production develops, leading to allergy symptoms.
Oranges and tangerines contain the most provocateur substances, so people prone to allergic reactions are advised not to consume these fruits. In lemons, the amount of allergens among citrus fruits is the smallest. Therefore, they rarely cause individual intolerance.
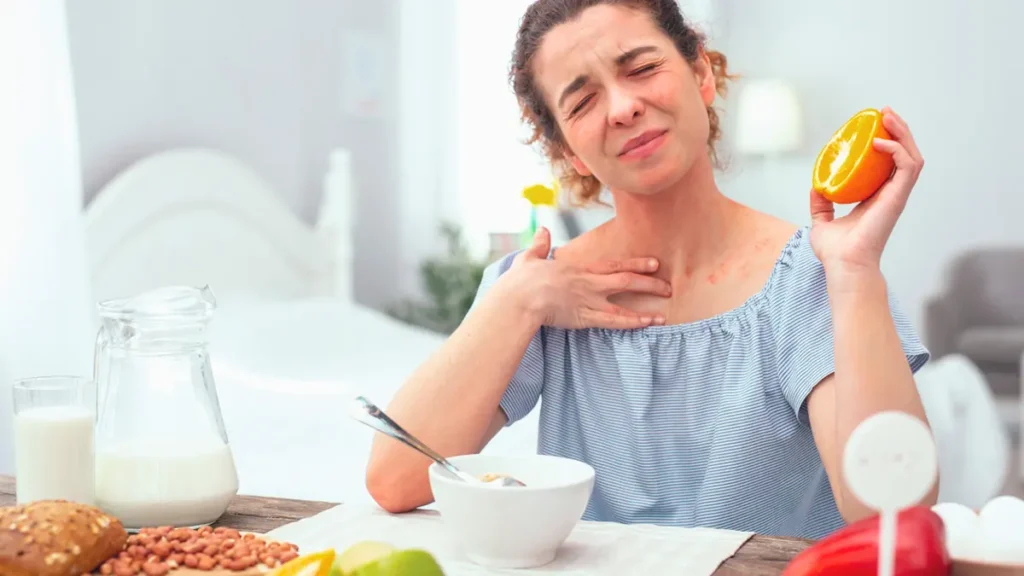

How to Recognize Citrus Allergy?
Usually, a citrus allergy manifests itself 2-3 hours after consuming the harmful product, but sometimes it can develop within minutes. Its main manifestations include:
- Redness and itching of the skin;
- Hives;
- Nasal congestion;
- Excessive tearing;
- Redness of the eyes;
- Headache;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting;
- Diarrhea.
These symptoms of citrus allergy can appear in any combination and have varying degrees of severity. In some cases, the patient may also experience additional manifestations such as:
- Dry, unproductive cough;
- Gastritis;
- Gastroenteritis;
- Cheilitis;
- Irritable bowel syndrome;
- Colitis;
- Atopic dermatitis;
- Bronchospasm;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Quincke’s edema;
- Anaphylactic shock.
Not always do you need to consume citrus fruits as food to develop an allergy. Some people only need to inhale its aroma. Essential oils contained in the pulp and peel of the fruits can irritate the mucous membranes of the nose, eyes, and upper respiratory tract. As a result, a person develops:
- Tearing;
- Allergic rhinitis;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Allergic cough;
- Bronchospasm.
If the allergy to tangerines or any other citrus is extremely strong, it is enough for a person to touch the fruit to get another exacerbation. In this case, the disease manifests itself in the form of local reactions (redness or itching of the skin, etc.).
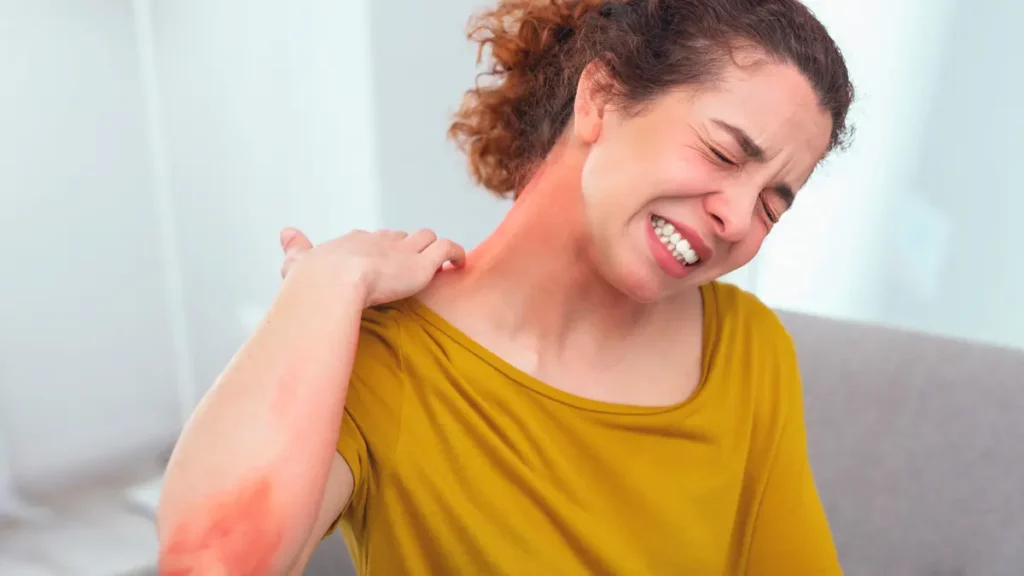

Diagnosing Citrus Allergy
Since the symptoms of citrus allergy are diverse and can mimic ARVI, gastrointestinal disorders, and other diseases, diagnosing the pathology on your own can be extremely difficult. To make the correct diagnosis, you first need to see a family doctor. The specialist will examine the patient and, if necessary, refer them to an allergist.
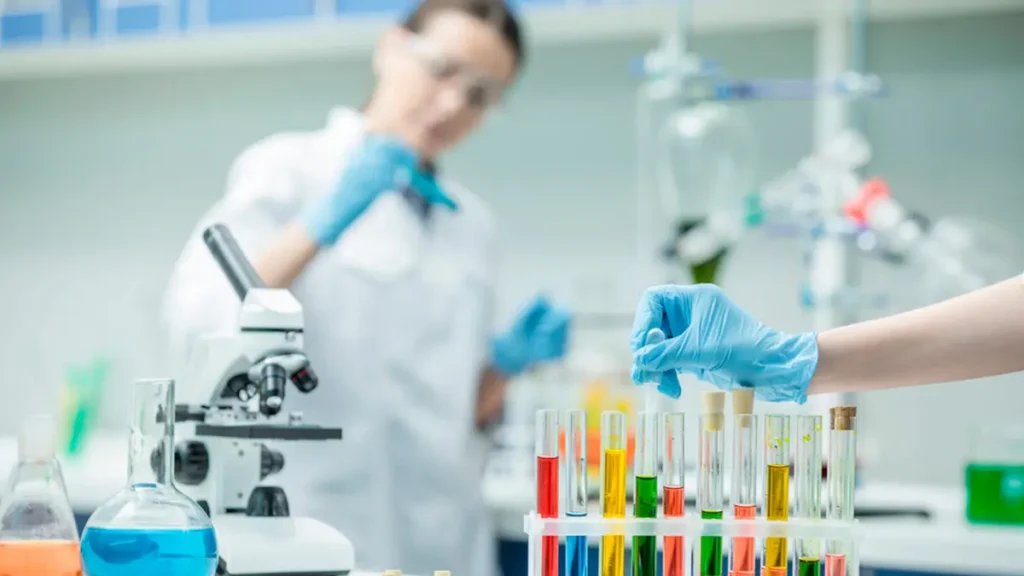
Diagnosing conditions related to an allergic reaction to citrus fruits involves several stages:
- Collecting anamnesis (talking with the patient, studying their medical records);
- Conducting a visual examination, identifying symptoms, and establishing a preliminary diagnosis;
- Conducting laboratory diagnostics (skin tests, blood tests for immunoglobulins, provocation tests, etc.);
- Evaluating the diagnostic results.
Usually, these steps are enough for the doctor to establish a final diagnosis.

How to Get Rid of Citrus Allergy: Treatment Features
Treating allergic conditions caused by increased sensitivity to citrus fruits aims to:
- Eliminate disease manifestations;
- Prevent relapses.
The therapeutic scheme is prescribed by an allergist, considering the patient’s general condition and the specifics of their disease. Usually, during the treatment of allergies, the following measures are taken:
- Medication therapy aimed at eliminating symptoms;
- Excluding citrus fruits and products and drinks containing them from the diet.
Only a doctor prescribes medication therapy. They create an individual medication intake schedule and determine the duration of its use.
Treatment of citrus allergy depends on the symptoms observed in the patient. In addition to antihistamines and enterosorbents, which are almost always prescribed, it may include nasal drops for treating allergic rhinitis, corticosteroid ointments for external treatment of itchy skin areas, antitussive drugs, etc.

It is not allowed to take any medications without a doctor’s permission, change dosages, or cancel treatment independently, as this can lead to a deterioration of the patient’s condition.
The diet for citrus allergy completely excludes the consumption of provoking products. Not only the fruits themselves are banned but also drinks containing their juice or extract, pastries with orange or lemon zest, etc. Allergy sufferers should also refrain from using essential oils that can irritate the mucous membranes and cause inflammatory processes. Medications containing components derived from citrus should not be taken either.
A diet for increased sensitivity to tangerines, limes, and other citrus fruits should always be followed. It should be remembered that even a small piece of the provoking fruit can trigger another allergy, so it is better to stay as far away from dangerous fruits as possible.
Citrus Allergy: A Video on Pathology Treatment
Watch a YouTube video about the mechanism, symptoms, risks, diagnosis, and treatment of allergic conditions.
Final Thoughts
Citrus allergy is a common disorder that can significantly impair quality of life and, in some cases, lead to serious complications. The main methods of diagnosis are laboratory tests, and treatment includes avoidance of allergens and drug therapy. It is important to see a doctor in time to prevent relapses and effectively control symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions and Answers About Citrus Allergy
An allergy to mandarins and other citrus fruits, often observed in early childhood, frequently resolves on its own as the child grows older. However, there are cases where it persists for life. It cannot be cured, so the only way to avoid symptoms is to abstain from citrus fruits.
Cetirizine, Loratadine, Fexofenadine, Desloratadine, Levocetirizine, Bilastine, Rupatadine. Any of these medications should only be taken after consulting a doctor.
Alcoholic beverages negatively affect the immune system, which is already compromised during an allergic reaction. Additionally, they can interact with medications prescribed for allergy treatment. Therefore, consuming alcohol is prohibited for individuals with any allergic manifestations.
It takes the body between 2 to 4 weeks to eliminate the allergens.
It most commonly appears as diathesis (redness of the skin on the cheeks and around the mouth). Other symptoms may include itching, peeling, dryness, and rashes on the skin.